Differences between helical gears vs spur gears
Gears can come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. Every type of gear has specific applications they’re ideal for, and typically gear designs vary enough that there isn’t much overlap. However, some gear types are rather similar in design and can be used in comparable applications. This blog will look at one such case — helical gears vs spur gears — explaining some of the differences between the two and the types of applications each are best suited for.
Spur Gears
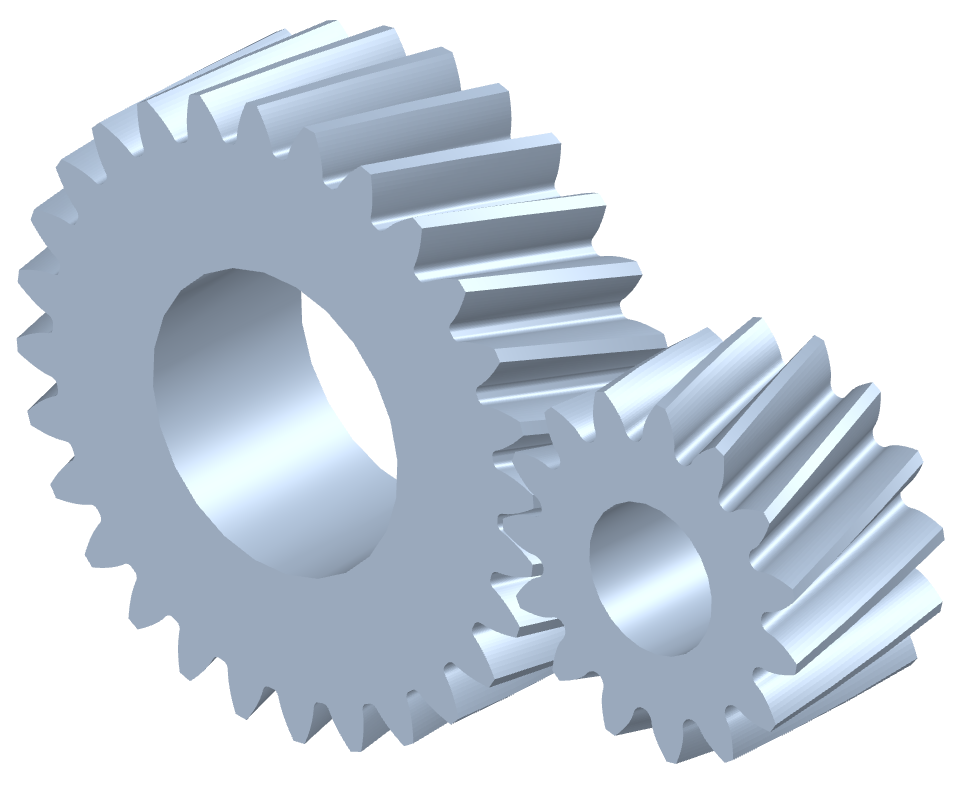
Spur gears are the most common type of gear. If you were to ask someone to describe what a gear looks like, they would almost certainly describe a spur gear. One reason for this would be the simplicity of its design; straight teeth that can interlock with other spur gears, evenly spaced around a circular body.
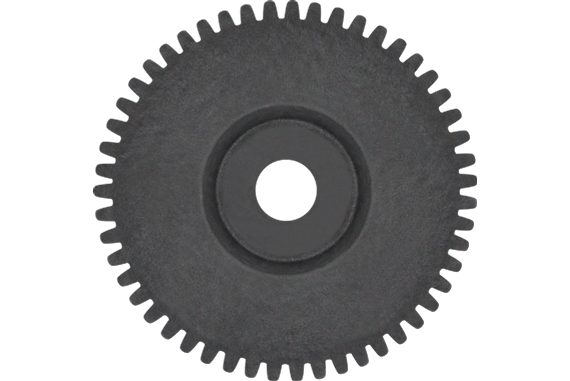
One of the advantages spur gears hold over helical gears is manufacturing cost. Thanks to the simplicity of design, spur gears are very cheap and quick to manufacture. The point of contact is also smaller with spur gears due to the straight design of the teeth, generating less friction and increasing efficiency. At higher speeds, however, spur gears generate much more noise and vibration than helical gears, making spur gears better suited for low-speed applications.
Helical Gears
Where helical gears differ from spur gears is the shape of the teeth; helical gears use angled teeth instead of straight teeth. This angle creates a larger, more gradual surface of contact between the gears, ensuring quieter and smoother operation than spur gears. The design also makes helical gears better suited for high-load applications. However, helical gears generate axial thrust due to the angular teeth, requiring either a thrust washer bearing or the combination of two helical gears to create a single gear, similar in design to a herringbone gear.