Star quad cables & their advantages over twisted pair cables
What are star quad cables?
Star quad cables, unlike traditional two-conductor cables, feature four conductors twisted together in a unique, star-like pattern. This specialized design is engineered to significantly enhance signal clarity by minimizing various forms of interference.
By balancing out noise picked up along the cable, star quad stranding ensures a cleaner and more reliable transmission, making it the preferred choice where interference is common and where performance cannot be compromised — most often in audio equipment or industrial applications.
What are the differences between the stranding methods?
There are three primary stranding options in cable production other than star quad stranding. These are twisted pair stranding, cores wound in layers, and cores wound in bundles.
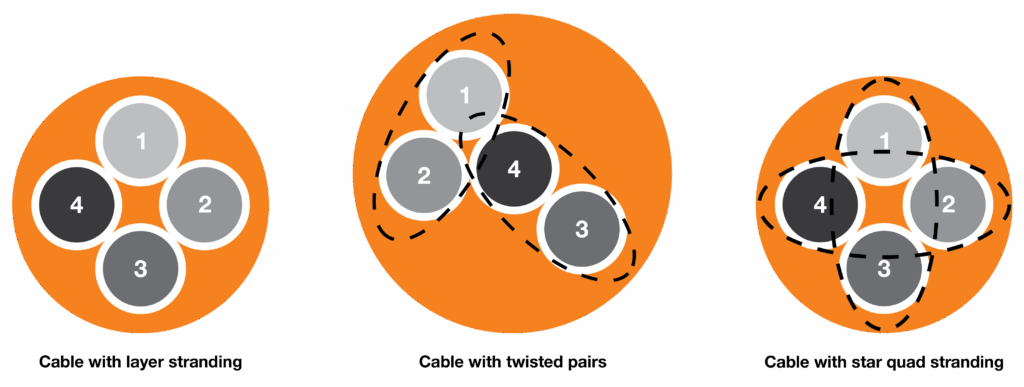
Cores wound in layers
Here the cores are stranded together in ascending order. This results in the following sequence: core 1, core 2, core 3 and core 4. These are a more affordable alternative to other cable stranding methods, but layered cables are more prone to permanent deformation due to material fatigue. This is most likely to take the form of a cable corkscrew, which is usually followed shortly by core rupture.
Related: 6 most common causes of cable failure
Layered cables are best used in applications with negligible crosstalk, as they are not designed to minimize crosstalk and instead focus on durability and cost-effectiveness. Cores wound in layers are not recommended for use in cables with more than seven cores; in these cases cores wound in bundles would be better suited and achieve a longer service life in moving applications.
Cores wound in bundles
Multi-core cables wound in layers are prone to corkscrews and core breakages, even when used within energy chains. The complex, multi-stranded interior of bundled cables eliminates these problems. Here, stranded wires are first twisted with a special pitch length, then twisted again to form single core bundles. These bundles are then re-stranded around a tension-resistant core.

This core stranding method ensures tensile and compression forces are equalized around the center core element. With its high tensile strength, it gives the stranded structure the necessary internal stability and ensures the stranding remains strong even under extreme bending stresses.
Twisted pair stranding
It is often necessary to transmit signals via two pairs of cores. This often creates the risk of signals in the core pairs influencing each other. This phenomenon is called near-end crosstalk. To counteract this, twisted pair stranding is used. Twisted pair stranding is achieved by twisting two cores together to form a pair and then stranding together those pairs of cores.
The disadvantage of this type of stranding is that the cable becomes thicker and less round than with cores wound in layers. For applications in energy chains, the cable diameter is important. An e-chain® offers only limited space and the bend radius of a cable is also determined by the outer diameter. Furthermore, a two-pair cable is mechanically not as stable as a cable with cores wound in layers.
Advantages of star quad stranding
Magnetic immunity
The unique quadrupole geometry of star quad cables provide them exceptional magnetic immunity. Opposite conductors are paired in a precise way that forms each leg of a balanced circuit. This pairing gives each leg an identical geometric center, and ensures any magnetic interference affects each leg equally to create a common-mode interference signal.
This common-mode signal can then be rejected by a balanced receiver to significantly reduce total magnetic interference. This reduction typically ranges from 10 dB – 30 dB, making star-quad cables ideal in environments with strong magnetic fields, such as near power cables or electrical equipment.
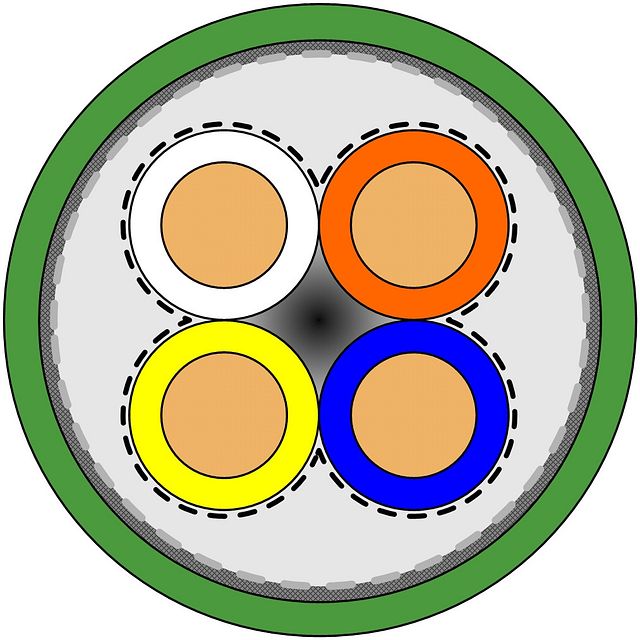
Cross-section of a continuous-flex star-quad cable from igus. Shop here
Noise rejection
The same quadrupole geometry that helps resist magnetic interference also provides superior noise rejection compared to standard twisted pair cables. Any noise that impacts one wire will be effectively balanced out by the opposite wire to prevent external interference from being transmitted as a disruptive signal. This results in cleaner, more reliable signal transmission, even in environments with high levels of background interference.
EMI/RFI rejection
Star quad cables are significantly more effective at blocking more electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) than twisted pair cables. The balanced configuration of conductors ensures any interference picked up by one conductor is canceled out by the opposite conductor. This advanced interference cancellation mechanism makes star quad cables ideal for applications where maintaining signal clarity is paramount, especially in electrically noisy industrial settings.
Disadvantages of star quad cables
The primary disadvantage of star quad cables compared to twisted pair cables is their higher capacitance. A star quad cable has roughly the same capacitance as a standard two-conductor cable of 50% greater length.
However, unless dealing with star quad cables of 100 meters or more in length, there should be no significant impact in the audio applications star quad is most often used in.
Star quad cables for industrial applications
While most often used in audio equipment, star quad cables can vastly improve the performance of more traditional industrial applications as well. With the capability to mitigate interference, star quad cables offer reliable performance even in the vicinity of large motors, variable frequency drives, power cables, and other electrical equipment often found in industrial applications.

Conclusion
Star quad cables, with their unique four-conductor twisted design, offer significant advantages in signal clarity and interference rejection due to their specialized geometry. While they excel in magnetic immunity, noise rejection, and EMI/RFI rejection compared to twisted pair cables, their main drawback is higher capacitance, though this is typically only a concern for very long runs. This makes them a preferred choice for applications where signal integrity is crucial, such as in audio equipment and industrial settings with high levels of electrical noise. Ultimately, for demanding applications where performance cannot be compromised, star quad stranding offers a superior solution, even providing mechanical benefits in moving applications.
Star quad cable FAQs
A star quad cable is a type of electrical cable that consists of four conductors twisted together around a central filler or core, with the conductors arranged in a symmetrical "star" pattern. This configuration is primarily designed to improve electromagnetic interference (EMI) rejection.
The primary advantages include:
- Superior Noise Rejection: Excellent common-mode noise rejection due to the cancellation effect of the opposing magnetic fields.
- Reduced RFI/EMI: Highly effective at minimizing interference from external sources like radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Improved Signal Quality: Leads to cleaner audio or data signals, especially over longer runs or in noisy environments.
- Lower Inductance: The geometry can contribute to lower overall inductance compared to other configurations.
While highly effective, some potential disadvantages include:
- Higher Cost: Generally more expensive than standard twisted pair cables due to the more complex construction.
- Larger Diameter/Less Flexible: Can be slightly larger in diameter and less flexible than simpler cables, depending on the gauge and jacket.
- More Complex Termination: Requires careful termination to ensure the benefits of the star quad configuration are realized.
The impedance of a star quad cable, like other cables, depends on its specific construction (conductor gauge, dielectric material, spacing). For audio applications, they are typically designed for low impedance balanced lines, usually around 110 ohms for digital audio or much lower for analog microphone/line level signals. For data, the impedance will be specified to match the application (e.g., 100 ohms for some data networks).
No, star quad cables typically use standard connectors appropriate for their application. However, the wiring within the connector must correctly implement the star quad pairing to maintain its noise rejection properties.
- Process Control: Connecting sensitive sensors (e.g., thermocouples, pressure transducers) to PLCs or control systems.
- Automation: Cabling for robotics, servo drives, and other automated machinery where precise control signals are crucial.
- Building Management Systems: For HVAC controls, security systems, and other sensitive signal runs within industrial or commercial buildings.
- Intercom/P.A. Systems: In large industrial facilities where long runs are needed and noise is prevalent.
- Data Acquisition: Connecting various instruments and data logging devices in electrically noisy areas.
While star quad cables significantly improve signal integrity in noisy environments, they generally do not eliminate the need for conduit, especially in applications where physical protection is required. However, they can reduce the need for shielded conduit or the expense of routing cables far away from noise sources.
While both use twisting for noise rejection, a standard twisted pair has two conductors. A star quad has four conductors, which are wired in two pairs (e.g., A+B and C+D) with opposite polarities. This unique geometry allows for superior common-mode noise rejection compared to a single twisted pair.
Star quad cables are commonly used in:
- Professional audio (microphones, line-level signals)
- Broadcast and recording studios
- Live sound reinforcement
- Industrial control systems (where signal integrity is critical)
- Data transmission in noisy environments
- Some specific types of sensor cabling
In a star quad, the four conductors are wired as two pairs, with the signal being carried by diagonally opposite conductors. Any external noise field induces an equal and opposite voltage in the two pairs, which effectively cancels out when the signals are summed at the receiving end.
Yes, they can be used for both. They are renowned for their performance with analog audio signals, but their noise rejection benefits also make them suitable for certain digital signal applications, particularly those requiring high integrity in noisy environments.
Industrial environments are often characterized by high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) from sources like:
- Heavy machinery (motors, VFDs)
- Power cables
- Welding equipment
- Fluorescent lighting
- Radio frequency equipment
Star quad cables provide a robust solution for maintaining signal integrity for sensors, control signals, and industrial communication networks in these noisy conditions, preventing data corruption and system malfunctions.
Yes, many manufacturers produce star quad cables specifically designed for industrial use. These often feature:
- Rugged Jackets: Made from materials like PVC, polyurethane (PUR), or TPE for abrasion, chemical, oil, and UV resistance.
- Shielding: In addition to the star quad configuration, they may include overall foil or braid shields for even greater EMI protection.
- Environmental Ratings: Designed to withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, and other harsh conditions.
- Compliance: Meeting specific industrial standards (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS).
While the star quad configuration intrinsically provides excellent common-mode noise rejection, proper grounding and additional shielding (e.g., an overall braid or foil shield connected to ground at one end) are still crucial in industrial environments. The star quad handles differential noise, while the external shield protects against common-mode noise and direct electrical interference before it can induce current in the conductors. Together, they offer comprehensive noise immunity.



